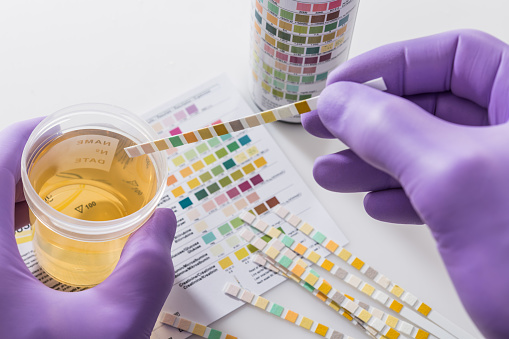
About the test
Urine analysis is a frequent and important test, performed during a routine check-up, for diagnostic purposes, during pregnancy as well as pre-operatively.
It is used for screening of urinary tract infections, kidney and liver issues as well as diabetes.
Urinalysis typically includes the following stages:
1: Sample inspection
2: Chemical dipstick test
3: Microscopic examination
1. Sample inspection
During this stage the healthcare provider evaluates the following aspects:
- Color
- Appearance
- Odor
2.. Chemical dipstick test
The dipstick test uses a chemical strip that is submerged in the sample and changes color when exposed to different substances. A dipstick test may be used to check various aspects of the urine sample including:
- Specific gravity
- pH
- Leukocyte esterase
- Nitrites
- Protein
- Glucose
- Ketones
- Urobilinogen
- Bilirubin
- Hemoglobin
3. Microscopic examination
After the sample is centrifuged, the sediment is examined microscopically for:
- White blood cells
- Red blood cells
- Bacteria
- Casts
- Crystals
- Mucous
- Lipid droplets
Sample
The first morning urine specimen is preferred.
Preparation
Before urination washing of the external genitalia with water and soap is required (Antiseptic soaps should be avoided). Rinsing of the area with abundant water and drying with a clean towel should follow.
Procedure
The urine sample should be midstream and collected in a special, sterilized container. It should be then transferred to the laboratory within an hour. If this is not possible the sample may be maintained in the fridge for up to four hours.
Toddlers: The sample is collected in special containers which look like small plastic bags.
Individuals with a permanent catheter: The area is disinfected and the sample is collected from the ureteral tube.
Evaluation of results and indicative pathologic findings
| Test parameter | Normal values | Possible meanings of abnormal values |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Color | Clear |
|
| Appearance | Light yellow to amber |
|
| Odor | Distinct, usually mild |
|
| Chemical characteristics | ||
| Specific gravity | 1005-1025 | Elevation:
Reduction:
|
| pH | 5-7 | Elevation (alkaline pH):
Reduction (acidic pH):
|
| Leukocyte esterase | Negative |
|
| Nitrites | Negative |
|
| Protein | Negative |
|
| Glucose | Negative |
|
| Ketones | Negative |
|
| Urobilinogen | Negative <0.1 | Elevation:
|
| Bilirubin | Negative |
|
| Hemoglobin | Negative |
|
| Microscopic characteristics | ||
| White blood cells | 0-2 per optical field |
|
| Red blood cells | 0-2 per optical field |
|
| Bacteria | Rarely present |
|
| Epithelia | Rarely present |
|
| Casts | Rarely present | Leukocytic:
Epithelial:
Erythrocytic:
Hyaline:
Granular:
Fatty:
|
| Crystals | Rarely present | ACIDIC URINE
Uric acid crystals:
Calcium oxalate crystals:
Cystine crystals:
Tyrosine crystals:
Leucine crystals:
ALKALINE URINE Calcium phosphate crystals
Ammonium urate crystals:
Magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals:
|
Additional information
- The first urine voided in the morning is preferred because of its high condensation as well as its acidic pH, factors that help preserve all urine elements.
- The sample must be collected in the middle of urination because, this way, the possibility of contamination with epithelial cells and bacteria carried away from the urethra at the beginning of urination, is reduced.